3D rendering is a revolutionary technology that brings virtual creations to life by transforming computer-generated models into realistic and visually stunning images. In various industries such as architecture, product design, and entertainment, 3D rendering has become an indispensable tool for visualizing concepts and presenting ideas. This article explores the basics of 3D rendering, its types, applications, advantages, challenges, future trends, and more.
Basics of 3D Rendering
Understanding 3D models
In the realm of 3D rendering, a model refers to a digital representation of an object or scene. These models are created using specialized software that allows designers to manipulate and shape virtual objects, defining their geometry, textures, and materials. By using sophisticated algorithms, these models can be transformed into realistic images.
Rendering process overview
The rendering process involves converting 3D models into 2D images by simulating the interaction of light with objects in a virtual environment. It encompasses various stages such as scene setup, modeling, texturing, lighting, and the final rendering. With the help of powerful computers and advanced rendering software, intricate details and lifelike visuals can be achieved.
Types of 3D Rendering
1. Photorealistic rendering aims to create images that closely resemble real-world objects and scenes. By simulating light, shadows, reflections, and materials accurately, photorealistic rendering produces visually stunning images that are almost indistinguishable from photographs.
2. Non-photorealistic rendering Non-photorealistic rendering, also known as NPR, focuses on creating artistic or stylized visuals rather than realistic ones. It can mimic various artistic styles, including sketch-like renderings, watercolor effects, or even abstract interpretations.
3. Real-time rendering is used in interactive applications such as video games and virtual reality experiences, where rendering must be performed in real-time to provide immediate feedback to the user. This type of rendering requires optimization techniques to balance visual quality with performance.
Tools and Software for 3D Rendering
Popular 3D rendering software
There are numerous software options available for 3D rendering, each with its own set of features and capabilities. Some popular choices include Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, Cinema 4D, and V-Ray. These tools provide designers with a range of options to create realistic and compelling visuals.
Popular 3D rendering software
There are numerous software options available for 3D rendering, each with its own set of features and capabilities. Some popular choices include Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, Cinema 4D, and V-Ray. These tools provide designers with a range of options to create realistic and compelling visuals.
Advancements in rendering technology
The field of 3D rendering continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in hardware and software. The introduction of ray tracing technology, which simulates the behavior of light more accurately, has significantly improved the quality of rendered images. Additionally, cloud-based rendering has emerged as a cost-effective solution, allowing designers to offload the rendering process to powerful remote servers.
Applications of 3D Rendering
Architecture and real estate
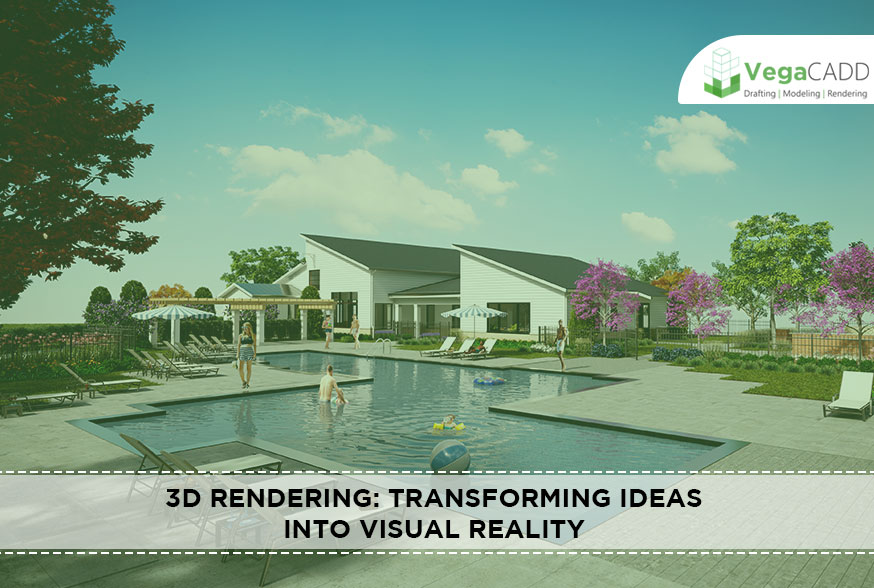
3D rendering plays a vital role in architectural design and real estate marketing. It enables architects to create realistic visualizations of buildings and interiors, helping clients visualize the final outcome. For real estate marketing, 3D rendering allows potential buyers to explore virtual walkthroughs of properties before they are built.
Product design and manufacturing
In product design, 3D rendering enables designers to visualize and refine concepts before physical prototypes are created. It aids in evaluating aesthetics, ergonomics, and functionality, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional prototyping methods. Additionally, 3D rendering facilitates the creation of product visuals for marketing materials and advertisements.
Entertainment and media
The entertainment industry extensively utilizes 3D rendering for visual effects in movies, TV shows, and animations. From creating fantastical creatures to breathtaking environments, 3D rendering brings imagination to life on the big screen. It also plays a crucial role in video game development, providing immersive and visually impressive gaming experiences.
Advantages of 3D Rendering
• Enhanced visualization
3D rendering offers a level of realism and detail that surpasses traditional 2D representations. By visualizing objects in a three-dimensional space, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of their designs, leading to better decision-making and improved communication.
• Time and cost savings
By enabling virtual prototyping and iterative design processes, 3D rendering significantly reduces the time and cost associated with physical prototyping. Designers can make modifications quickly, evaluate different options, and receive feedback before committing to physical production.
• Iterative design process
3D rendering allows designers to explore multiple design iterations easily. With the ability to make changes to the virtual model on the fly, designers can experiment with different materials, colors, and textures to achieve the desired outcome. This iterative design process enhances creativity and leads to better final designs.
Challenges in 3D Rendering
Computational requirements
Creating realistic 3D renderings requires substantial computational power. Rendering complex scenes with intricate details and advanced lighting effects can be computationally intensive and time-consuming, necessitating high-performance hardware or cloud-based rendering solutions.
Realistic lighting and texturing
Achieving realistic lighting and texturing is a challenge in 3D rendering. Simulating the behavior of light accurately and replicating the properties of various materials convincingly requires expertise and attention to detail. Skillful manipulation of lighting and texture parameters is crucial to achieve photorealistic results.
Rendering optimization
As scenes become more complex, optimizing rendering times becomes essential. Techniques such as level of detail (LOD) management, occlusion culling, and multi-threaded rendering can help improve performance. Balancing visual quality with acceptable rendering times is a constant challenge for 3D rendering professionals.
Future Trends in 3D Rendering
Ray tracing technology
The integration of ray tracing technology into real-time rendering is an exciting development in the field. By simulating the physical behavior of light more accurately, ray tracing produces realistic reflections, shadows, and global illumination. As hardware improves, real-time ray tracing is expected to become more accessible and commonplace.
Virtual reality integration
With the growing popularity of virtual reality (VR), the integration of 3D rendering with VR experiences is becoming more prevalent. Realistic and immersive environments can be created by combining 3D rendering techniques with VR technology, providing users with interactive and lifelike virtual worlds.
Cloud-based rendering
Cloud-based rendering offers scalable and cost-effective solutions for computationally intensive rendering tasks. By offloading the rendering process to powerful remote servers, designers can access significant computational resources without the need for expensive hardware. This trend is expected to continue as cloud infrastructure and rendering services evolve.
Conclusion
3D rendering has revolutionized the way we visualize and bring ideas to life. From architecture to product design and entertainment, its impact can be seen across various industries. The ability to create realistic and compelling visuals, coupled with time and cost savings, makes 3D rendering an invaluable tool for designers and businesses alike. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more realistic and immersive experiences through the ongoing evolution of 3D rendering.
Contact us here for 3D Rendering Services that transform your imagination into reality.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between 3D rendering and 3D modeling?
A: While 3D modeling involves creating digital representations of objects or scenes, 3D rendering is the process of converting these models into realistic 2D images or animations by simulating light and materials.
Q: Can 3D rendering be used for animations?
A: Absolutely! 3D rendering plays a crucial role in creating animations, whether for movies, video games, or other forms of digital media. It allows animators to bring characters and environments to life with lifelike visuals and stunning visual effects.
Q: How long does a typical rendering process take?
A: The time required for rendering varies depending on several factors, including the complexity of the scene, the level of detail, the desired quality, and the available hardware resources. Simple scenes may render in minutes, while highly complex and detailed scenes can take hours or even days.
Q: Is 3D rendering only limited to computer-generated images?
A: While 3D rendering is most commonly associated with computer-generated images, it can also be applied to other fields. For example, scientific simulations and medical imaging often utilize 3D rendering techniques to visualize complex data and structures.
Q: Can 3D rendering be used for scientific simulations?
A: Yes, 3D rendering is widely used in scientific simulations to visualize complex data and phenomena. It allows researchers and scientists to gain insights and communicate their findings more effectively by rendering visual representations of scientific concepts and simulations.